Indoor Wood Furnace Boilers: A Detailed Guide
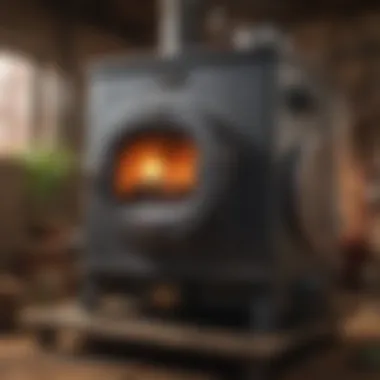

Overview of the Topic
Indoor wood furnace boilers have gained appreciable attention in recent years, particularly for those who are keen on reducing their carbon footprint while advocating for sustainable heating solutions. These systems not only provide an eco-friendly alternative to conventional fuels but also leverage readily available biomass resources, showcasing the intersection of sustainability and practicality.
Understanding the mechanics of these boilers, along with their benefits and potential drawbacks, is essential for anyone considering such a move. Homeowners and professionals alike are increasingly reevaluating their heating strategies in response to rising energy costs and growing awareness of environmental concerns.
Foreword to the Key Natural Resource or Environmental Issue Being Discussed
In a world grappling with climate change, the reliance on fossil fuels remains a pressing issue. This reliance contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, which in turn exacerbates global warming and various environmental disturbances. Indoor wood furnace boilers present a unique solution to mitigate these challenges by harnessing renewable energy from wood, a resource that can be sustainably managed.
Moreover, wood heating is often regarded as a more favorable option compared to propane or electric heating, especially in regions abundant in timber resources. Highlighting the need for sustainable practices in energy consumption is crucial as we move toward a greener future.
Background Information on the Significance of the Topic
The significance of indoor wood furnace boilers extends beyond mere cost savings. They offer versatility in fuel sources, utilizing residues from forest management practices that would typically be left to decompose and release CO2 back into the atmosphere. Furthermore, advancements in boiler technology have led to more efficient systems that minimize emissions and maximize heat output. This is particularly important as communities strive to balance energy needs while protecting their natural resources.
Adopting wood heating solutions aligns with broader environmental goals. By promoting better land management and reducing reliance on carbon-heavy fuels, these systems have the potential to play a pivotal role in sustainable energy transitions. The call for integrating eco-friendly heating options into our homes is more than a trend; it’s a vital step toward fostering resiliency against climate change.
Prologue to Indoor Wood Furnace Boilers
Indoor wood furnace boilers are emerging as a pivotal solution in our quest for sustainable energy. In a world grappling with increasing energy costs and environmental concerns, these systems present a feasible alternative for heating buildings while being kind to the planet. This section will explore the significance of indoor wood furnace boilers, illuminating their role in the modern heating landscape.
Defining Indoor Wood Furnace Boilers
So, what exactly are indoor wood furnace boilers? Simply put, these systems are designed to burn wood efficiently to generate heat and hot water for residential purposes. They operate by combusting wood logs or pellets within a closed chamber, using a boiler to transfer heat to water, which is then circulated to provide warmth throughout the home.
These boilers come in various sizes and configurations, adapting to different needs and architectural styles. What’s more, they can be installed as standalone units or integrated into an existing heating system, providing versatility in heating solutions. The core benefit here is that they can harness a renewable resource—wood—offering an independent alternative to conventional energy sources.
In essence, these boilers not only provide heating but can also significantly lower utility bills while reducing one’s carbon footprint.
Historical Context and Evolution
The evolution of indoor wood furnace boilers is deeply rooted in the history of human innovation and adaptation. For centuries, wood was the primary source of heat. However, as societies industrialized, fossil fuels took center stage, leaving wood heating to fade from the limelight. Yet, this trend has seen a reversal in recent years, driven by a resurgence of interest in greener and more sustainable energy practices.
In the late 20th century, the development of more efficient combustion technologies gave rise to modern wood boilers. These units are not your grandparent's fireplace; they are engineered to maximize combustion efficiency and minimize emissions. Over time, advancements in materials and controls have improved their reliability and user-friendliness, making them increasingly popular among environmentally conscious homeowners.
Today, the push for reducing greenhouse gases and reliance on fossil fuels has sparked a renewed interest in these systems. The modern indoor wood furnace boiler signifies the marriage of tradition and technology, granting us the ability to enjoy the warmth of a wood fire while maintaining a low ecological impact.
"The journey towards efficient wood heating solutions reflects our broader commitment to energy independence and sustainability."
Through this exploration, it becomes evident that indoor wood furnace boilers stand as a beacon of practicality and environmental stewardship. As we delve further into the intricate workings, benefits, and future of these systems, we prepare to uncover how they can meet today’s heating challenges while charting a more sustainable future.
Understanding the Mechanism
Understanding how indoor wood furnace boilers operate is crucial for anyone considering this heating solution. By grasping the mechanics behind these systems, users can better appreciate their benefits and make informed decisions. This section dives deep into the components that make these boilers work and the combustion processes that render them effective.
Components of Indoor Wood Furnace Boilers
Indoor wood furnace boilers are complex machines designed to convert wood into heat efficiently. Each part plays a vital role in this transformation. Here are some key components worth noting:
- Furnace Body: This is the core structure of the boiler, usually made of heavy steel or cast iron. It houses the combustion chamber where wood is burned. The design here dictates heat retention and transfer.
- Chamber: Within the furnace body, the combustion chamber is where the magic happens. It’s designed to provide optimal airflow and wood placement for complete combustion.
- Heat Exchanger: Essential for transferring heat from the burning wood to the water or air that circulates in your home. A well-designed heat exchanger can significantly increase the system's efficiency.
- Flue and Chimney: These parts are responsible for venting out smoke and gases produced during combustion. An effective exhaust system prevents backdrafts and keeps indoor air quality intact.
- Circulator Pump: A circulator pump moves warmed water through your heating system, ensuring that every corner of your home benefits from the heat produced.
- Control Systems: Modern boilers often come equipped with sophisticated control systems that monitor temperature and fuel supply, helping to optimize combustion and efficiency.
These components collectively work in harmony to create a heating system that’s not just effective but also reliable. Understanding their interactions can aid in troubleshooting and maintenance, enhancing the overall longevity and performance of your boiler.
How Combustion Works
The combustion process in indoor wood furnace boilers relies on three fundamental elements: fuel, heat, and oxygen. Properly understanding how these elements come together ensures optimal performance and efficiency.
- Fuel Selection: The type of wood used greatly influences combustion. Hardwoods, like oak or hickory, are dense and yield higher heat output compared to softwoods. This choice of fuel impacts not just the amount of heat generated but also the amount of ash produced.
- Oxygen Supply: Efficient burning of wood requires sufficient oxygen. When the combustion chamber is designed with ample airflow, it allows the wood to burn at higher temperatures, leading to more efficient heating and less smoke. A well-balanced air supply results in cleaner combustion, reducing harmful emissions while maximizing heat output.
- Heat Generation: As wood combusts, it generates heat and produces gases. The thermal energy produced raises the temperature of the surrounding water or air in the boiler. This is where the heat transfer occurs, moving warmth throughout the living space.
"When wood burns efficiently, it's more than warmth; it's a renewable source of energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels."
It's essential to manage these factors effectively. Regular checks can ensure optimal combustion conditions, maximizing efficiency and minimizing down-the-line issues.


Through this exploration of mechanisms and components, homeowners can appreciate the inner workings of indoor wood furnace boilers. Not only does this knowledge bolster proactive upkeep, but it also prepares one to make sound decisions in selecting and using these heating systems.
Benefits of Using Indoor Wood Furnace Boilers
Indoor wood furnace boilers have gained a reputation as a highly efficient and sustainable heating solution for many households. The merits of utilizing these systems extend beyond mere warmth; they touch on financial, environmental, and energy independence aspects that resonate with a growing audience concerned about their ecological footprint. By exploring these benefits in detail, we can better understand why more individuals and families are considering this option in their quest for reliable home heating.
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most compelling arguments for indoor wood furnace boilers is their cost-effectiveness. While the initial setup cost may raise eyebrows, the long-term savings can outweigh those initial investments significantly. For instance, wood is often cheaper than oil or natural gas, and in areas with abundant forestry, it's possible to source wood at little to no cost. This leads to lower monthly energy bills.
Consider this example: A family using propane might spend several hundred dollars monthly during winter months. In contrast, those utilizing wood boiler systems often see their costs drop dramatically, sometimes spending only a fraction of that amount. Additionally, when budgeting for heating, it's wise to factor in the potential for price fluctuations in fossil fuel markets, which is less relevant for wood.
But, the benefits don't stop at savings. Indoor wood furnaces can enhance the overall value of a property. Prospective homebuyers increasingly favor energy-efficient homes, and a well-installed wood furnace can serve as a selling point.
Sustainability and Renewable Energy
In an age where people are becoming increasingly aware of climate issues, indoor wood furnaces stand out as a renewable energy source. Wood is considered carbon-neutral; when trees grow, they absorb carbon dioxide, which they then release back into the atmosphere when burned. This cycle has a less adverse impact on our environment compared to traditional fossil fuels. It's a natural process, allowing households to heat their homes while contributing to a closed ecological loop.
Moreover, utilizing local wood resources supports sustainable forestry practices. Many forest management programs aim to ensure that logging activities do not exceed regrowth capacities, promoting healthier ecosystems. By chooseing indoor wood heating, users are often choosing to be responsible custodians of the land.
- Local sourcing promotes community jobs and reduces transportation emissions, making the heating system even greener.
- Recycling wood waste, like tree limbs or sawdust, can serve as fuel, reducing landfill waste.
Independence from Conventional Energy Sources
Dependence on conventional energy sources for heating can be a significant concern for many households. Indoor wood furnace boilers provide a solution that gives users a sense of independence and security. In a world where energy prices can fluctuate wildly due to geopolitical tensions or natural disasters, those using wood furnaces often feel less vulnerable.
Imagine a scenario where a winter storm knocks out electricity or causes fuel shortages. Those who rely on gas or electric heating systems may find themselves in the cold, but wood furnace owners have a buffer. Well-stacked, seasoned firewood ensures warmth can be maintained regardless of external pressures.
This autonomy doesn't just apply to fuel; it also fosters a greater sense of control over one’s environmental impact. Users can choose sustainable sources for their wood and decide how much they want to consume, aligning their heating practices with their values.
Ultimately, the benefits of using indoor wood furnace boilers go far beyond merely heating a home. From financial savings to sustainability and independence, these systems offer an array of virtues that appeal to environmentally-driven individuals and families alike. Investing in such a system often leads to not just a warmer home, but a more exciting and responsible relationship with energy consumption.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of indoor wood furnace boilers is a crucial aspect to discuss, especially as society shifts towards more sustainable heating solutions. As fossil fuels dwindle and climate change concerns heighten, understanding how these systems contribute—or detract—from ecological balance becomes paramount. Indoor wood furnace boilers can play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions when managed and operated correctly. However, their benefits must be weighed against potential drawbacks, making it imperative to address both sides of the equation.
Carbon Emissions Comparison
When evaluated against traditional heating options like oil or natural gas systems, indoor wood furnace boilers present a unique profile. The primary advantage lies in their ability to utilize biomass, a renewable source of energy. During the combustion of wood, the carbon released was once absorbed by trees during their lifespan. In this respect, wood heating has a circular carbon cycle, which is inherently more sustainable than burning fossil fuels, where carbon stores are released into the atmosphere that hasn't been part of the recent biological cycle.
Consider the following points when comparing carbon emissions:
- Wood vs. Fossil Fuels: According to several studies, modern wood stoves produce significantly lower levels of emissions than older, traditional wood burning methods. Innovative designs in indoor wood boilers enhance efficiency, allowing for cleaner combustion with reduced particulate emissions.
- Lifecycle Assessment: A comprehensive comparison must factor in the entire lifecycle of the energy sources. While fossil fuels become more carbon-intensive at extraction and transportation stages, sustainably harvested wood can be integrated into long-term land management and environmental stewardship practices.
- Air Quality Considerations: Still, it’s worth mentioning that while indoor wood furnace boilers produce less carbon dioxide overall, they might emit other particles that can affect air quality. Thus, having efficient filtration and good chimney designs can help mitigate these emissions.
Ultimately, while indoor wood furnace boilers generally create lower carbon footprints, it’s essential to employ responsible practices to maximize their environmental advantages.
Sourcing Sustainable Wood
Finding sustainable wood sources is integral to ensuring the positive environmental impact of indoor wood furnace boilers. While using wood as a heating source offers ecological advantages, how this wood is sourced makes all the difference. If done irresponsibly, it can lead to deforestation and habitat loss, undermining the benefits that wood heating brings.
Here are some considerations for sourcing sustainable wood:
- Certification Programs: Look for wood certified by organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or the Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI). These programs ensure that the wood comes from responsibly managed forests, promoting biodiversity and preventing overharvesting.
- Local Sourcing: Choosing local wood can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with transport. Plus, local sourcing often means quicker access to high-quality, renewable materials.
- Recycling Wood: Utilizing reclaimed or recycled wood can also be a sustainable choice. Not only does it prevent unnecessary logging, but it also puts byproducts from other industries to good use.
- Community Involvement: Engaging with local forestry or community action groups can provide insights into best practices in wood sourcing. This collective approach fosters a sense of responsibility and stewardship among those using indoor boilers.
By focusing on sustainable practices in wood sourcing, users can ensure that their choice of heating not only warms their homes but also contributes to the health of the planet.
Efficiency Standards and Ratings
In the field of heating solutions, particularly when discussing indoor wood furnace boilers, efficiency standards and ratings play a crucial role in informing consumers and professionals alike. These metrics not only help in evaluating the performance of wood furnaces but also assist in making informed decisions that impact both the environment and one’s wallet. This section aims to explore key elements of efficiency ratings, shedding light on their significance and the considerations they bring into focus.
Understanding Efficiency Ratings
Efficiency ratings are essentially numerical values that indicate how effectively a heating system converts fuel into usable heat. The common measurement unit for wood furnaces is the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE), which is expressed as a percentage. This figure captures the amount of heat that is generated compared to the energy content of the fuel consumed.


A high AFUE rating suggests that a furnace uses less wood to produce the same amount of heat compared to a lower-rated model. For instance, an indoor wood furnace with an AFUE of 85% means 85% of the energy from the wood contributes to heat production while the remaining 15% is lost, primarily through exhaust and other inefficiencies.
Choosing a model with a higher efficiency rating can lead to significant savings in fuel costs over time and may also contribute towards lower emissions. Each percentage point above a baseline level translates to savings; therefore, consumers should aim for models that have ratings above 75% for optimal performance.
Regulatory Standards and Guidelines
Regulatory standards govern the manufacturing and operation of indoor wood furnace boilers, ensuring they meet certain efficiency and environmental criteria. In many regions, manufacturers must comply with specific guidelines that dictate everything from emissions levels to safety features. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set forth regulations that manufacturers must adhere to for their products to enter the market.
The following are key standards:
- Emission Limits: These limits define how much particulate matter and other pollutants can be released from wood boilers.
- Testing and Certification: Manufacturers must undergo rigorous tests to prove their products meet efficiency and emissions standards.
- Safety Guidelines: These dictate installation protocols, maintenance requirements, and safety features to protect users and properties from potential hazards.
"Regulations ensure that consumers receive efficient and environmentally-friendly appliances, but they require manufacturers to step up their game in terms of technology and design."
Before purchasing an indoor wood furnace boiler, one should always check for compliance with local regulations to ensure the model exceeds the minimum efficiency standards. This conscientious approach not only supports a sustainable future but also safeguards one’s investment by opting for products that are both efficient and compliant with the law.
Installation Considerations
When it comes to maximizing the effectiveness of indoor wood furnace boilers, installation considerations play a pivotal role. Selecting the right setup not only influences the system’s efficiency but also ensures safety and compliance with regulations. This section delves into two significant areas: choosing the right location and understanding necessary safety measures.
Choosing the Right Location
The location for installing an indoor wood furnace boiler is not just a matter of convenience; it significantly affects operation and safety. Here are some critical points to consider when determining the ideal spot:
- Proximity to Wood Supply: Being close to your wood storage means less labor in hauling fuel. Imagine lugging heavy logs across the house every time you restock! A nearby storage option will make life easier.
- Airflow and Ventilation: Proper airflow is crucial. A congested space might lead to smoke accumulation or insufficient combustion air. Look for a spot with good ventilation; this promotes efficiency while minimizing harmful emissions.
- Clearance Requirements: Depending on your boiler's design, maintaining specific clearances from walls, ceilings, and combustible materials is essential. This isn’t just a recommendation; it’s often mandated by building codes. Make sure to double-check the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid fitting your boiler into a tight squeeze, which could lead to disaster.
- Support Structure: Wood boiler systems can weigh a ton, so ensure that the floor can handle the load without sagging. A solid base is essential to prevent structural instability.
- Accessibility for Maintenance: Place the boiler where there’s easy access for routine maintenance. It might be tempting to tuck it away in a corner, but if you can’t get to it, you may end up with problems because maintenance schedules can easily get sidelined.
This thought-through spot could make all the difference when the first cold snap hits.
Safety Measures and Regulations
Installing an indoor wood furnace boiler comes with a slew of safety measures that must be adhered to. Ignoring regulations can lead to serious problems, not to mention potential fines or legal issues. Here’s what to keep in mind:
- Local Codes: Research your local building codes related to heating systems. These codes often specify requirements for installation, emissions, and more. Don’t be caught off guard — following the rules from the get-go is key.
- Chimney Configuration: An efficient and safe chimney setup is critical. Follow manufacturer guidelines for height, flue size, and slopes to ensure proper exhaust. Failure to configure this properly can lead to backdrafting, which is not just annoying — it can be dangerous.
- Carbon Monoxide Detectors: As a precaution, have carbon monoxide detectors installed in the house and near the boiler. Detecting harmful gas early can save lives.
- Fire Extinguishers: Position at least one fire extinguisher nearby, specifically rated for wood and solid fuel fires. You can never be too prepared, right?
- Training and Knowledge: Lastly, ensure everyone who interacts with the system understands how it operates and the safety measures in place. Knowledge is power — or, in this case, safety.
Understanding the nuances of proper installation helps you not just get heat but also peace of mind, making indoor wood furnace boilers a viable option for homeowners looking for efficient heating.
Maintenance and Care
Maintaining an indoor wood furnace boiler is crucial for ensuring its longevity and effectiveness. Just like a good car that needs regular oil changes, your boiler requires regular care to function optimally. Neglecting maintenance can lead to inefficiencies and not to mention safety hazards. Let’s face it, a poorly maintained unit can make your home feel more like a sauna on a hot summer day than a cozy haven in winter.
For folks invested in sustainable heating options, routine care not only protects your investment but also maximizes efficiency. A well-maintained boiler can harness heat better, ensuring your firewood doesn’t just go up in smoke. In this section, we’ll break down the essentials of keeping your indoor wood furnace boiler in peak condition.
Routine Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance involves a series of systematic checks and repairs. Here are some practices to consider for your indoor wood furnace boiler:
- Clean the Ash Pits: Ash buildup can block airflow. A monthly cleaning keeps the fire burning efficiently.
- Inspect the Chimney: A clean chimney is vital for smoke to exit. Have it checked and cleaned at least once a year to prevent creosote build-up, which can lead to chimney fires.
- Check Seals and Gaskets: Over time, seals can wear out. Inspect and replace as necessary to maintain airtightness.
- Test Water Levels: If your system uses water, check the levels regularly. Low water can cause overheating.
- Examine Boiler Settings: Adjust the settings according to the weather. An efficient boiler works smarter, not harder.
Adopting these practical habits not only helps you stay warm but is also a responsible step toward energy conservation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with regular maintenance, hiccups can happen. Here are some common issues that may arise and how to address them:
- Insufficient Heat Output: If you’re noticing a chill in the air, check for ash buildup or a blocked chimney. Either could be the culprit.
- Smoke Backdraft: This unsettling situation can occur if your flue is blocked or if the chimney is not drawn properly. Ensure that your chimney cap is intact and ventilation is clear.
- Water Leaks: Water leaks can point to a crack in your boiler or worn-out seals. Act quickly to avoid permanent damage to your system and home.
- Unusual Noises: Sounds such as banging or gurgling could indicate air pockets in the system. Consider bleeding the radiators to release trapped air.
Regular attention to these potential issues can save you both money and frustration down the road.
Comparing Alternative Heating Methods
Understanding the various heating methods available today serves not just for mere comparison but also for informed decision-making in energy consumption. By evaluating different heating systems, one can uncover not only the cost implications but also their environmental consequences. With indoor wood furnace boilers positioned as a sustainable option, examining alternatives such as oil, gas, electric, and solar heating is fundamental to comprehending the full scope of heating solutions.
Oil and Gas Heating Systems


Oil and gas heating systems have long been staples in many households. They offer reliable warmth but come with notable drawbacks. For one, the dependence on fossil fuels enables fluctuating prices and potential supply constraints. This adds a layer of unpredictability to budgeting for heating, a privilege that many seek to avoid. Moreover, these systems generally present a larger carbon footprint due to the emissions they generate.
When it comes to efficiency, oil systems can heat spaces quickly, but their overall energy efficiency often trails behind modern wood boiler technologies. The interplay between price volatility and environmental sustainability often leaves consumers at a crossroads. While convenient, the ecological impact raises fundamental questions about long-term viability.
"The future may not favor fossil fuels as society shifts toward more renewable options; understanding this shift is crucial for financially responsible heating solutions."
Electric Heating Solutions
Electric heating systems have garnered attention for their ease of use and installation simplicity. There are various types, from baseboard heaters to electric furnaces. They can be particularly useful for homes without access to gas lines or those aiming to minimize emissions. However, they can place a heavy burden on one's energy bill, especially during peak usage times.
Another point of concern lies in the source of electricity. If the electricity is generated from fossil fuels, the net environmental benefit may be negligible. Transitioning toward more renewable energy sources, such as wind or hydropower, could improve sustainability but may not be the case everywhere. There's also the life expectancy of electric heating solutions, which often require more frequent replacements compared to their wood-fired counterparts.
Solar Heating Options
Solar heating systems represent a fascinating avenue, harnessing the sun's free energy to reduce costs. Whether via solar panels or thermal heating systems, they offer a renewable solution. Yet, challenges do exist. The initial investment can be hefty, and the efficiency of solar systems highly depend on geographical location and sunlight exposure throughout the year.
Another consideration is the technology's ability to integrate with existing heating systems. Many households may find a hybrid solution appealing, combining solar with traditional heating methods to ensure consistent warmth during winter months. As advancements in solar technology evolve, they might offer more compelling options, but they also come with their own set of concerns regarding performance and maintenance.
In examining these diverse systems, it becomes clear that each method has its merits and drawbacks. Thus, the choice of heating system must align with individual goals in sustainability and economic feasibility. Engaging with these options empowers consumers to make choices that can lead to greater energy independence and environmental responsibility.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Regulatory and compliance issues play a crucial role in the implementation and operation of indoor wood furnace boilers. Navigating these regulations ensures that users not only maximize efficiency in heating but also adhere to environmental standards and safety protocols. Understanding these laws can save users from potential legal headaches and improve the overall performance of their heating systems.
Local and State Regulations
Local and state regulations surrounding indoor wood furnace boilers can vary widely based on geography and climate considerations. For instance, regions with stricter air quality regulations may impose limitations on the type of wood used or the emissions produced by these systems. In many locales, specific permits are required before installation.
Homeowners need to check with local authorities to ensure compliance. Here are some key aspects of local rules:
- Permitting: Most states require a permit for indoor wood furnace installation, which protects community safety and health.
- Emissions Standards: Specific limits on smoke and particulate matter emissions may dictate appliance efficiency rates and required features.
- Zoning Laws: These could restrict where you can install a wood furnace in your property—be mindful of distance from property lines and water sources.
It's advisable to contact local building inspectors or environmental agencies to gain insights specific to your location.
Environmental Compliance Standards
Environmental compliance standards are designed to minimize the impact of heating systems on the ecosystem. These can include regulations on
- Wood Sourcing: Sustainability and legality of wood sources is critical. Many regions promote using only wood accredited by environmental groups.
- Particulate Emission Limits: Often expressed in grams per hour, these limits help mitigate air pollution caused by wood burning. The lower the emissions, the better for the environment.
- Regular Monitoring: Compliance may also necessitate periodic testing of emissions from the appliance. Tracking this ensures adherence to standards over time.
Meeting these standards is essential, not just for legality but also for modifying and improving practices among users. A well-maintained and compliant indoor wood furnace can serve a dual purpose—providing heat while being a good steward of the environment.
Keeping up-to-date with regulations is critical for anyone considering or currently using an indoor wood furnace boiler. Ignoring these can lead to fines, costly retrofits, or even replacement.
In summary, the landscape of regulations is complex, but understanding it helps ensure a smoother operation and encourages sustainable practices within communities. Compliance is not just about following the law; it's about fostering a responsible relationship with nature.
Future of Indoor Wood Furnace Boilers
As we look ahead, the landscape of heating solutions is evolving. The future of indoor wood furnace boilers holds significant importance not just for individual users but for the broader context of energy consumption and environmental sustainability. The advancements in technology paired with a growing awareness of eco-friendly options are influencing how these systems will be designed and utilized. This section will delve into various elements that shape this future, focusing on innovations and shifts in consumer preferences.
Innovations in Design and Technology
The innovation wave in the heating industry shows no signs of slowing down. Indoor wood furnace boilers are at the forefront of cutting-edge technology which aims to make them more efficient and user-friendly. Manufacturers are now incorporating smart technology, allowing homeowners to monitor their systems remotely.
Some noteworthy advancements include:
- Automated combustion control: This ensures optimal burning conditions which maximizes fuel efficiency and minimizes emissions.
- Improved insulation materials: Enhanced insulation in these units reduces heat loss, making them significantly more efficient.
- Modular designs: Some newer models come in modular formats, allowing for scalability depending on the heating needs.
- Integration with renewable energy systems: There's an emerging trend to pair wood boilers with solar panels to enhance energy independence and reliability.
These technologies not only appeal to consumers looking for efficiency but also contribute positively to the environment by reducing the carbon footprint associated with heating.
Shifts in Consumer Preferences
Today's consumers are more environmentally conscious than ever before. The choice to opt for indoor wood furnace boilers is increasingly influenced by a desire for sustainability. Many users are now actively seeking products that align with their values, particularly connected to the use of renewable resources and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Factors impacting these shifts include:
- Environmental awareness: Consumers are more informed about the impact of their choices. This increased awareness translates into a preference for heating solutions that are perceived as greener.
- Financial incentives: Government programs and tax breaks for using renewable heating systems encourage homeowners to invest in wood boilers.
- Aesthetic considerations: Modern designs are being tailored to fit seamlessly into contemporary homes, making them not just functional but also stylish.
"As the world moves towards a sustainable future, the role of indoor wood furnace boilers will become increasingly pivotal, merging tradition with innovation."
These trends show that as society progresses, so too will the technology and consumer attitudes surrounding indoor wood furnace boilers, making them a central player in the heating market. Attention to future developments in this area can help stakeholders make informed decisions, ultimately benefiting both people and the planet.



