Understanding the Migration Patterns of Canada Geese


Overview of the Topic
Understanding the migration patterns of Canada geese offers a window into a complex interaction among climate, ecology, and animal behavior. These waterfowl are not merely seasonal travelers; they embody a suite of environmental cues and adaptations finely tuned over millennia. Knowing their migratory routes can help us comprehend not only the birds themselves but also the broader ecological landscape they inhabit.
Prologue to the Key Environmental Issue
Canada geese migrate annually between breeding and wintering grounds, which can cover thousands of miles. Their journey implicates various environmental factors, such as seasonal changes in temperature, food availability, and habitat conditions. However, this natural cycle is increasingly disrupted by climate change, altering migratory behavior and affecting their populations.
Background Information on the Significance of the Topic
The significance of studying their migration lies both in environmental science and conservation. By better understanding the routes Canada geese take and the ecological roles they fulfill, we can assess their contributions to ecosystems and the potential consequences if these patterns are interrupted. As social animals, geese also symbolize the health of their habitats.
Current Status and Challenges
Canada geese populations have grown in some areas, thanks to urbanization, which provides ample feeding ground. However, this increase has also led to overpopulation in certain regions, resulting in heightened human-wildlife conflicts.
Examination of the Current State of the Natural Resource Concern
The current status of Canada geese reflects a dual narrative. In some localities, populations are stable or rising, while in others, habitat loss and climate impacts pose serious threats. The habitat alongside lakes, rivers, and wetlands is particularly vulnerable, as urban development continues to encroach on these environments.
Identification of Challenges and Threats Facing the Topic
- Urbanization - Encroachment on natural habitats has narrowed the spaces available for migration and nesting.
- Climate Change - Altered weather patterns can shift food supplies and habitat availability, forcing geese to adapt rapidly.
- Human Interference - Conflicts arise when geese populate urban parks and private properties, leading to calls for population control measures.
- Ecosystem Imbalance - Overpopulation can disrupt local ecosystems, as excessive grazing leads to habitat degradation.
Sustainable Solutions
To tackle these pressing issues, several sustainable practices and community-led solutions can be explored.
Exploration of Sustainable Practices and Solutions
- Habitat Restoration - Restoration of wetland areas can provide conducive environments for breeding and foraging.
- Community Involvement - Local communities play a pivotal role in monitoring and protecting migration routes. Engaging schools and local groups in conservation activities can foster awareness.
- Research Initiatives - Ongoing studies into geese behavior and population dynamics are crucial for adaptable management plans.
Showcase of Successful Case Studies
- In one notable instance, the restoration of the Salton Sea in Southern California has been beneficial for migratory birds, including Canada geese. Increased vegetation cover and habitat protection can be seen as a blueprint for other regions.
- Programs in Canada focusing on educational outreach have improved understanding and tolerance towards local geese populations, leading to more harmony between wildlife and urban settings.
Impact and Importance
The impact of these migratory patterns extends beyond just the geese themselves. They influence local ecosystems, affecting predator-prey dynamics, plant communities, and nutrient cycling.
Analysis of the Impact on Ecosystems and Communities
Understanding the movements of Canada geese aids in grasping the broader ecological web. As primary consumers, their grazing can shape vegetation patterns, affecting habitat for other species. Communities also face repercussions from changes in population dynamics, often needing to adapt management strategies based on shifting migratory behaviors.
Emphasis on the Importance of Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts aimed at protecting migratory routes and habitats are paramount. Promoting ecologically balanced environments ensures that both Canada geese and their supporting ecosystems remain safeguarded for future generations. Such initiatives underline not just the importance of these graceful birds but also the rich tapestry of life they are a part of.
"Migration is more than just a journey; it's an intrinsic part of survival that shapes communities and ecosystems."
In summary, seeing Canada geese as indicators of ecological health enables us to better understand the intricate web of life that thrives around us. Being astute observers of these seasonal travelers can lead us toward sustainable practices that ensure their continued presence in our ever-evolving landscapes.
Understanding Canada Geese
The study of Canada geese is not just about appreciating their beauty and grace; it's about grasping how they function within our ecosystems. These birds carry the essence of migratory behavior, showcasing resilience and adaptability in the face of environmental challenges. Learning about Canada geese allows us to unravel the complex interplay between migration patterns and ecological health. It adds a layer of understanding to conservation efforts and the impacts human activity has on wildlife.
Species Overview
Canada geese belong to the Anser canadensis species. Commonly found across North America, they are easily recognizable by their blackheads, white cheeks, and brown bodies. These geese exhibit a range of subspecies, with the most familiar one being the Canada Goose that is often seen in parks and waterways. To communicate, they use an array of honks, which play vital roles in coordinating during migration and establishing territory. The adaptability of Canada geese to various environments makes them a fine example of wildlife thriving in urban spaces, while they still hold their natural instincts.
Habitat Preferences
The habitat of Canada geese is as varied as their migratory routes. They prefer wetland areas, including marshes, lakes, and rivers. However, they have increasingly made their homes in suburban parks and golf courses, where grassy areas provide an easy food source. The influences of climate, human development, and competing species all shape where Canada geese settle and migrate. Factors like accessibility to water and availability of food significantly impact where these geese choose to live. It’s fascinating how they can adapt their habits to fit both natural habitats and urban environments, relying on both the wilderness and human-made landscapes for sustenance.
Physical Characteristics
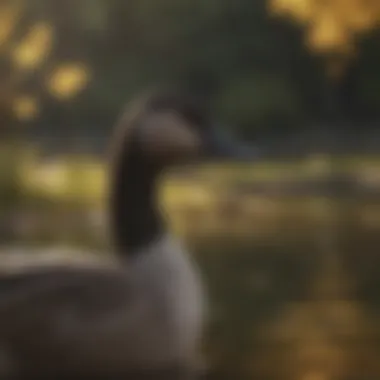

Canada geese are striking creatures, typically measuring about 30 to 43 inches long. They possess large wingspans that can reach up to 6 feet, which aid immensely in long-distance migrations. The male and female geese, though similar in appearance, can usually be distinguished by size, with males being somewhat larger. Their plumage is well-suited for camouflage amidst the reeds and seasonal foliage, offering protection from predators.
“The physical attributes of Canada geese serve not only as a means of survival in the wild but also play significant roles in their mating displays and social interactions.”
During the breeding season, their plumage may show slight variations, especially in the colors and markings around the head. This seasonal change reinforces their roles in mating rituals and social structure. Their unique morphology directly relates to their migratory success and adaptation to diverse climates, illustrating how every migration effort hinges on their physical readiness.
The Mechanics of Migration
The dynamics of migration in Canada geese is a topic that demands attention due to its profound implications on both their survival and the environments they inhabit. Understanding the mechanics of migration involves delving into the intricate motivations, timing, and energy considerations that these magnificent birds face during their seasonal journeys. Recognizing these factors can ultimately assist conservation efforts and promote a deeper understanding of their ecological role.
Motivations for Migration
Canada geese migrate primarily to seek suitable habitats that provide essential resources for survival, specifically food and breeding opportunities. During the colder months, the availability of water and forage diminishes, prompting these birds to embark on a quest for sustenance. The drive to migrate is not purely instinctive but is also influenced by learned behaviors passed down through generations. It’s as if they possess an embedded map, guiding them toward warmer regions where food is plentiful and predation risks are lower. This seasonal journey can be seen as a survival strategy crafted over millennia.
Timing and Seasonal Patterns
The timing of migration is critical and varies according to geographic location. Generally, Canada geese begin their southward journey in the fall, often around late September to early November, depending on climatic cues and regional temperatures. What’s interesting is that these birds have an uncanny ability to sense temperature changes and daylight variations, which serve as natural indicators for their migratory departure. Conversely, the return trip typically occurs in early spring, around late February to early April. This cyclical pattern underscores their reliance on environmental signals, ensuring they time their migration perfectly for breeding opportunities in their northern habitats.
"Migration is not merely about getting from one place to another; it's about the timing and conditions that allow for survival and reproduction."
Energy Requirements
Migration is no light feat, requiring substantial energy reserves. Plus, Canada geese must be incredibly strategic about how they utilize their metabolic resources. Before migration begins, many geese enter a phase known as hyperphagia, where they significantly increase their food intake to build fat stores. These fat reserves act as fuel for their long flights. During migration, they typically fly in a V-formation, which not only conserves energy through aerodynamic efficiency but also facilitates communication within the flock. Flight duration and conditions are carefully calculated, as adverse weather can lead to increased energy expenditure, jeopardizing their journey.
Migration Routes of Canada Geese
The migration routes of Canada geese are crucial for understanding their seasonal movements. These routes not only dictate the geese's travel between breeding and wintering habitats but also help in discerning the ecological impacts of their migration. Knowledge of these routes sheds light on the interactions of these birds with their environment, highlighting key areas that require conservation efforts. Identifying migration patterns aids in implementing effective strategies to protect critical habitats.
North American Flyways
North America is divided into four primary flyways that Canada geese utilize during their migratory journeys: the Atlantic, Mississippi, Central, and Pacific flyways. These corridors are akin to highways in the sky, offering geese safe pathways teeming with resources such as food and rest.
- Atlantic Flyway: This route stretches from the Arctic regions down to Florida. The migration along this corridor enables geese to exploit the diverse wetlands and estuaries the East Coast offers.
- Mississippi Flyway: This thoroughfare runs through the heart of the continent, allowing geese to access both agricultural and natural habitats that provide sustenance during long migrations.
- Central Flyway: This pathway serves as a vital link between Canada and the U.S. Great Plains. It offers critical stopover sites, especially in states like Nebraska, where wetlands are abundant.
- Pacific Flyway: This flyway spans the western region, providing migratory routes along the West Coast. Here, geese can access rich coastal estuaries and agricultural fields.
Understanding these flyways is essential for conservationists to protect these vital routes and the habitats lying along them.
Coastal vs. Inland Routes
When Canada geese embark on their journeys, they often face a choice between coastal and inland routes. Each path has its advantages and disadvantages, influencing the geese's migration behavior and ecological impact.
- Coastal Routes: These routes are popular as they provide access to abundant resources like marshes and estuaries. The proximity to the ocean also offers favorable weather conditions. However, the risks increase due to urban development and human activities, making it crucial for conservationists to monitor and protect these areas.
- Inland Routes: These pathways, while offering fewer resources, lead to less disturbed habitats compared to coastal routes. Geese utilizing inland routes may have to face longer distances between food sources, which demands more energy. The balance between risk and resource availability plays a significant role in determining which route a flock may choose.
The choice between these routes underscores the adaptability of Canada geese to their surrounding environments, often dictated by weather conditions and available resources.
Key Stopover Locations
During their lengthy migrations, Canada geese take necessary breaks to rest and feed at key stopover locations. These sites are crucial for the geese to replenish energy and ensure the survival of their young during the migration season.
Some significant stopover locations include:
- Chesapeake Bay: This area provides excellent foraging opportunities with its rich aquatic vegetation.
- Great Lakes: Offering an abundance of food sources and shelter, the lakes serve as pivotal points for geese migrating across the Midwest.
- Missouri River: The river’s wetlands are a magnet for thousands of geese, where they find ample resources to fuel their migration.
- Sierra Nevada Foothills: In California, these locations attract many geese, showcasing the importance of diverse habitats in migration.
Stopover locations are not merely rest stations; they’re lifelines that play a crucial role in the migratory success of Canada geese.
In sum, the migration routes of Canada geese are a fascinating blend of environmental factors and migratory behavior. Each component—from the flyways they traverse to the choices between coastal and inland routes—paints a comprehensive picture of their migratory patterns, reflecting an intricate relationship with their habitats.
Environmental Factors Influencing Migration
The migration of Canada geese is profoundly influenced by environmental elements. The way these birds navigate their seasonal journeys hinges on multiple factors, from climatic conditions to resource availability. Understanding these influences sheds light on their migratory behavior, essential for appreciating both their ecological role and the implications for conservation efforts in a shifting climate.
Weather and Climate Patterns
Weather plays a crucial role in the migratory patterns of Canada geese. They rely on favorable wind conditions as they fly long distances. Ideal weather can make the difference between a successful migration or a disastrous one. For example, a strong headwind can lead to increased fatigue and energy depletion. On the other hand, tailwinds can assist them, allowing the birds to cover greater distances efficiently.
The timing of migration also correlates closely with temperature changes. These birds often start their journey when the days begin to lengthen and temperatures warm. Warmer weather signals the onset of spring, triggering the migratory impulse to reach northern breeding grounds. Inhabiting regions where winter temperatures drop significantly forces them to move southward when food sources dwindle.
Availability of Resources

Resources are another central consideration for Canada geese during migration. These birds require abundant food and safe resting spots for refueling. Wetlands, agricultural fields, and lakes serve as vital waypoints, where they can replenish their energy reserves. If these resources become scarce due to drought or poor agricultural practices, geese might find themselves struggling to complete their migration.
Moreover, migratory routes should offer a reliable food source. In areas where habitat loss has occurred, the availability of food can become severely limited. This goes hand in hand with the competition they face from other species that rely on the same resources. Consequently, geese adapt their paths, seeking areas with sufficient accessibility to food and rest.
Impact of Urbanization
Urbanization poses significant challenges to the migratory behaviors of Canada geese. Expansion of cities often displaces natural habitats, transforming wetlands into urban landscapes. This process reduces the available resources that are critical for these geese during their journey. Not only do they face habitat loss, but urban environments can also be hazardous. Roads, buildings, and increased human activity disrupt their migrational patterns and present risks of collision and predation.
While some adaptations have occurred, such as forming populations in urban parks, these settings often lack the necessary resources for long-term sustenance.
"Migration is a dance with nature; misstep due to environmental shifts can lead to catastrophe."
Challenges faced by Canada Geese during Migration
Understanding the obstacles that Canada geese face while undertaking their arduous migratory journeys is crucial for grasping the broader implications of their survival and adaptability. These challenges affect not only individual geese but also have cascading effects on ecosystems, conservation efforts, and even local economies that benefit from these migratory birds. A deep dive into predation risks, human encroachments, and climate change effects reveals a gritty world wherein these birds must constantly navigate threats, adapt, and strive for survival amidst changing circumstances.
Predation Risks
Predation presents a significant hurdle for gooses in transit. When they fly in V-shaped formations, they might be less vulnerable to aerial predators like eagles or hawks. However, the distances they cover leave them exposed to ground-based threats as well, such as coyotes and foxes, especially when they stop to rest and feed. This can become a deadly game of cat and mouse, where the geese must remain vigilant.
- Survival Strategies: Geese often gather in large groups during migratory stops. The more eyes there are, the better chance they have of spotting an approaching predator. Their honks serve as alert signals that warn others of potential danger.
- Seasonal Risks: Interestingly, whether migratory birds face more threats can depend on the seasons; during spring migrations, for example, the foliage is often denser, potentially providing safer stopover locations. Conversely, some late fall migrations occur when food resources are scarce, forcing geese into more exposed areas.
Human Encroachments
As cities expand and agricultural practices change, the habitats of Canada geese are being compressed. Urbanization presents a dual-edged sword.
- In some ways, urban areas provide easy food access, such as parks and golf courses. However, these man-made landscapes usually lack the critical resources they need for nesting and resting.
- Collisions and Disturbances: Aside from habitat loss, geese also face threats from human activity like vehicle collisions. Their stopover sites can also become crowded with people, reducing their access to resting spaces, which is vital for energy replenishment.
"The migration of Canada geese is not merely a seasonal journey; it is a complex interaction between natural instincts and human influences."
Climate Change Effects
In an era of rapid climate changes, the migratory patterns of Canada geese are not immune. For one, shifting climates affect food availability, weather patterns, and nesting times.
- Sea Level Rise: Coastal geese are particularly vulnerable to rising sea levels. As their habitat decreases due to flooding, they face greater competition for dwindling resources.
- Temperature Variability: Changes in temperature can lead to mismatched migration schedules and breeding cycles. If geese arrive at their breeding grounds too early or late, they may miss the optimal environmental conditions needed for raising their young.
In summary, Canada geese face a multifaceted set of challenges during their migrations. From predation risks that require vigilance and strategy to human-related disruptions and the looming threat of climate change, the road ahead is fraught with obstacles. Addressing these issues is not only vital for the health of Canada geese populations but is also critical for fostering a more balanced ecosystem amidst human influence.
The Ecological Importance of Migration
Migration is not just a seasonal trek for Canada geese; it’s a pivotal part of the ecological tapestry in which they exist. As these birds travel thousands of miles to seek warmer climates, they perform roles that benefit ecosystems in profound ways. Understanding this ecological importance sheds light on the symbiotic relationship between migratory patterns and environmental health.
Role in Ecosystem Health
Canada geese contribute significantly to the health of ecosystems during their migration. Their movements impact vegetation and wildlife, providing a ripple effect that enriches the environments they inhabit. When they arrive at a new location, their feeding habits can help maintain plant growth by controlling species spread. For instance, when they graze on grasses and sedges, it prevents these plants from overcrowding other species, allowing for a diverse range of flora. This, in turn, supports a variety of fauna, creating a balanced habitat.
Moreover, geese are essential in seed dispersal. They consume berries and seeds during their journey, which are then excreted in new locations, fostering growth in places where certain plants may not be found otherwise. This natural distribution of plant life enhances biodiversity, meaning that the migration of Canada geese plays a critical role in ecosystem resilience.
Contributions to Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the backbone of a healthy environment, and Canada geese serve as key players within this framework. Their migratory cycles help facilitate complex interactions among various species. By nesting in varied habitats seasonally, they create opportunities for different organisms to thrive. The places they choose to stop or settle often experience spikes in species diversity due to the geese's presence.
Additionally, the social structures within their flocks can affect other wildlife. For instance, the presence of Canada geese can draw attention from potential predators, which in turn influences the behaviors of smaller birds or mammals in the vicinity. They also provide forage material for other animals that rely on the remnants of their feeding. The interdependence illustrated here emphasizes their role as a connector within ecosystems.
Nutrient Cycling
Nutrient cycling is crucial for maintaining ecosystem vigor, and Canada geese play a surprising role in this process. Their foraging habits lead to a natural redistribution of nutrients through their droppings. This waste is packed with nitrogen and phosphorus, which are essential for plant growth. When geese gather in large numbers, the levels of these nutrients can increase dramatically in specific areas, resulting in richer soils that promote the growth of plants.
Furthermore, during migration, geese often stir up the soil as they search for food. This activity contributes to aerating the ground, allowing other plants to establish roots more easily. In essence, they enhance the productivity of the ecosystems they migrate through, leading not only to immediate benefits, but long-term sustainability of those habitats.
"The migration of Canada geese is not just about the birds themselves, but about the vital roles they play in shaping their environments and ensuring ecosystem health."
In summary, the ecological importance of migration for Canada geese stretches far beyond their physical travel. Their influence on ecosystem health, contributions to biodiversity, and role in nutrient cycling position them as integral components of the environments they traverse. Recognizing these multifaceted roles helps bolster the argument for more attention toward their conservation, especially given the rapid environmental changes we are witnessing.
Conservation Efforts for Canada Geese
The preservation of Canada geese is a matter of increasing urgency, especially as their seasonal movements are intricately tied to broader environmental shifts. Conservation efforts focused on this species are not just beneficial; they are essential for maintaining ecological balance. These initiatives seek to mitigate the threats these birds face, from habitat loss to climate change.

Current Conservation Programs
Several programs work tirelessly to protect Canada geese and their habitats. One of the most notable is the North American Wetlands Conservation Act which funds projects aimed at restoring wetlands. Wetlands are not just a stopover spot; they are critical for feeding and breeding. The restoration of these areas helps not only the geese but also numerous other wildlife species.
In parks and wildlife reserves, monitoring projects have been set up to track population numbers and migration patterns. These programs involve data collection through field research and community involvement, allowing for a two-way exchange of information. Volunteers often assist with banding juvenile geese, providing valuable insights into survival rates.
Public Awareness Initiatives
Raising awareness plays a crucial part of the conservation strategy. Organizations have launched campaigns that educate people about Canada geese’s role in the ecosystem. For example, local workshops and community programs discuss the importance of preserving wetlands. Informative materials often highlight the connection between human activity and the challenges faced by the geese.
Another effective way to engage the public is through social media platforms. Posts on sites like Facebook and Reddit share experiences of sightings, encouraging people to appreciate the beauty and significance of these birds. Hashtags like #SaveTheGeese help generate interest and spread awareness rapidly.
Future Directions in Conservation
Looking ahead, the approach to conserving Canada geese must evolve. One potential direction involves incorporating climate impact assessments in conservation programs. Understanding how climate change affects habitat availability and food resources will be key in developing effective strategies.
Moreover, enhancing collaboration between different stakeholders—government agencies, conservation nonprofits, and local communities—could amplify efforts. Everyone has a stake in ensuring that these iconic migratory birds continue to thrive for years to come.
"The conservation of Canada geese serves as a bellwether for the health of our entire ecosystem. When we protect them, we protect the intricate web of life they are a part of."
Research and Tracking Methods
Research and tracking methods are crucial in understanding the migration patterns of Canada geese. The behaviors exhibited by these birds during their seasonal journeys provide invaluable insights into their ecological needs and the factors impacting their survival. With appropriate methods in place, researchers can gather data that informs conservation strategies and helps predict shifts in migration affected by climate changes.
Technological Advances in Tracking
In recent years, technology has transformed the way ornithologists study migratory patterns. GPS and satellite tracking have become indispensable tools. These devices allow researchers to monitor the precise movements of individual geese over vast distances. Not only do GPS tags provide real-time location data, but they also help to identify key migratory routes and stopover sites that the geese favor.
Moreover, the integration of data from various platforms, such as weather databases and ecological models, enhances the understanding of migration dynamics. Researchers can see how environmental factors directly influence migration timing and patterns.
"The advent of technology has allowed us to think beyond traditional observation. Now, we can track geese in a way that was unimaginable a decade ago."
— Dr. Emma Hargrove, Avian Migration Specialist
Citizen Science Contributions
Citizen science plays a vital role in gathering extensive data on Canada geese. Enthusiasts from different backgrounds participate in projects that involve observing and reporting sightings. This grassroots approach helps expand the geographic scope of research while introducing an element of community involvement in conservation efforts.
Platforms such as eBird allow amateur birdwatchers to submit their observations, thereby providing a plethora of data that can help track population trends and distribution changes over time. Contributing to these projects enhances public awareness and encourages community engagement with nature.
Data Collection Efforts
The systematic collection of data cannot be overstated when examining migration. Longitudinal studies tracking populations provide a wealth of information on survival rates and migration success. Traditional methods involve field observations and banding, which have their merits but are limited in scope.
Incorporating technology with traditional methods provides a more comprehensive view. Data can now include:
- Seasonal movement patterns
- Habitat selection at different life stages
- Responses to environmental changes
This multidimensional approach enriches the body of knowledge surrounding Canada geese and allows for proactive conservation strategies based on scientific evidence.
Overall, employing robust research and tracking methods is essential in deciphering the complexities of Canada geese migration. These efforts collectively inform conservation initiatives, ensuring these incredible birds continue their migratory journeys well into the future.
Cultural Significance of Canada Geese
Canada geese, known for their honking calls and distinctive V-shaped flight formations, play a significant role beyond their ecological impact; they are also cherished figures in various cultural contexts. Understanding their cultural significance enriches our appreciation of these birds and underscores the interconnectedness of wildlife and human societies.
Symbolism in Indigenous Cultures
In many Indigenous cultures, Canada geese are more than just birds; they represent values like community, cooperation, and resilience. Tribes that have inhabited areas where these geese migrate often weave their presence into stories and oral traditions. For example, the Iroquois view the goose as a symbol of loyalty and partnership. These birds are often featured in ceremonies signaling the change of seasons, marking important times for harvesting and community gatherings.
Further, the migration of the geese serves as a natural calendar. Their arrival and departure play a guiding role in the traditional actions of tribes. As the seasons shift, the geese signal when to plant crops or prepare for winter, emphasizing their role as environmental indicators. This relationship illustrates a deep cultural respect for wildlife and nature.
Representation in Literature and Art
Canada geese have also graced the pages of literature and works of art, transcending their role as mere wildlife to become symbols of broader themes. In poetry, they often represent migration and change, serving as metaphors for journeys in life. For instance, in some narratives, the resilience of geese during migration is paralleled to human struggles, showcasing endurance and adaptability.
Artists, from traditional painters to contemporary sculptors, have depicted these birds in various forms. Artists celebrate their elegance and instinctual drive to migrate, often capturing the harmonious connection between nature and humanity. Geese in flight can evoke feelings of freedom and the beauty of instinctual journeys, striking a chord with viewers and reminding them of their place within the natural world.
Role in Outdoor Recreation
For many people, Canada geese are integral to outdoor recreational activities. Birdwatchers and nature lovers flock to parks and lakes to observe these geese as they nest, migrate, and engage in social behaviors. The presence of Canada geese often encourages appreciation for the natural habitats they occupy, fostering a connection between humans and the environment.
Hunting is another facet of outdoor recreation where geese are prominent. Waterfowl hunting is a traditional practice for many, while it also serves contemporary recreation and conservation efforts. Managed regulated hunting can help maintain healthy populations, preventing overcrowding and helping sustain the ecosystems that both the geese and humans rely on.
The cultural ties to Canada geese are a vivid reminder of the intricate relationships between wildlife and human history.



